Static Routing 1
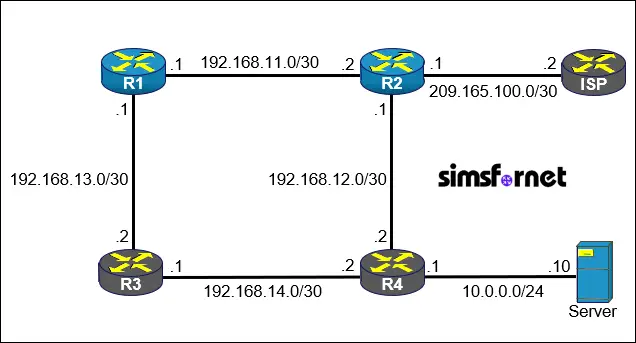
Topology
Tasks:
You are tasked with configuring static routes for a small network consisting of four routers: R1, R2, R3, and R4. The network includes an ISP connection and a server located on a LAN behind R4. R3 and R4 are fully configured and inaccessible. No dynamic routing protocols should be used.
- Configure default routes on R1 and R2 to forward all unknown traffic to the ISP.
- Configure host route on R1 to ensure that R1 prefers the path through R3 for traffic destined to the server.
- Configure a backup route on R1 with AD of 2 to use R2 as a secondary path to reach the server if the link between R3 and R4 fails.
Solution:
Task 1: Configure default
routes on R1 and R2 to forward all unknown traffic to the ISP.
To forward all unknown
traffic to ISP, we need two default routes.
On R1:
R1#configure
terminal
R1(config)#ip
route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.11.2
This command configures a
default route on R1, using R2 as the next hop (192.168.11.2). When R1 receives
traffic destined for an address not in its routing table, it will forward the
traffic to R2.
On R2:
R2#configure
terminal
R2(config)#ip
route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.100.2
This command configures a
default route on R2, using the ISP's IP address (209.165.100.2) as the next
hop. When R2 receives traffic destined for an address not in its routing table,
it will forward the traffic to the ISP.
Task 2: Configure host
route on R1 ensure that R1 prefers the path through R3 for traffic destined to
the server.
Host routes are specific
routes that direct traffic to a single destination IP address and are
configured with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255 (/32), meaning a single
address or a specific node.
On R1:
R1(config)#ip
route 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 192.168.13.2
This route ensures that R1
forwards traffic destined for the server (10.0.0.10) to R3.
Since R4 is already
configured, it should have a route in place to reach back to R1.
Task 3: Configure a backup
route on R1 with AD of 2 to use R2 as a secondary path to reach the server if
the link between R3 and R4 fails.
A backup route is used only
when the primary route becomes unavailable. It is configured with an
Administrative Distance (AD) higher than the primary route. By default, the AD
of a static route is 1.
On R1:
R1(config)#ip
route 10.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 192.168.11.2 2
This command configures a
backup static route to the server (10.0.0.10) via R2 with an administrative
distance of 2, which is higher than the default AD of 1. As a
result, this route will only be used if the primary route (via R3) becomes
unavailable
Now exit the configuration
mode and save the configuration.
R1(config)#end
R1#write
memory
R2(config)#end
R2#write
memory
Packet Tracer File
Clicking this button will begin the download of a ZIP file. Inside the ZIP file, you'll find a Packet Tracer Activity (.pka) file, which will automatically track your progress as you configure the network.

