ACL Config 2
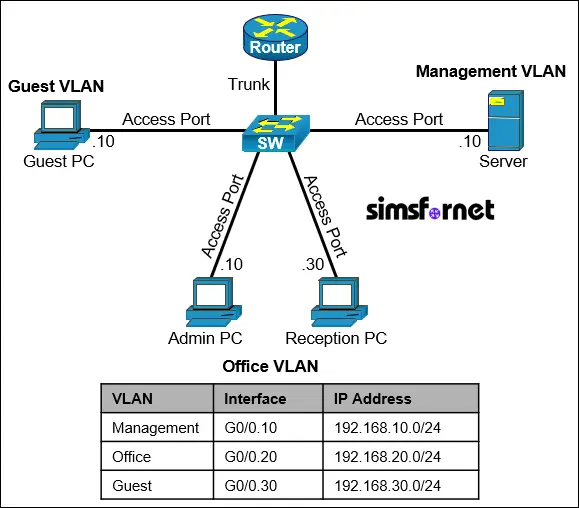
Topology
Tasks:
IP connectivity is established. The company is using a Router-On-A-Stick (ROAS) network for its office and aims to secure the network by restricting access to certain services in VLANs.
- Create a NACL named OFFICE_ACL on the appropriate device in the network.
- Block all telnet traffic from entering into the Management VLAN.
- Allow all traffic From the Admin PC into the Management VLAN.
- Block SSH traffic from the Reception PC to the Management VLAN but allow all other traffic.
- Allow HTTP traffic from the Guest VLAN to the Management VLAN.
- Block all other traffic to the Management VLAN.
- Apply the Access List to the appropriate device interface.
Solution:
Task 1: Create a
NACL named OFFICE_ACL on the appropriate device in the network.
We will create the
ACL on the router as it is routing traffic between VLANs..
Router#configure
terminal
Router(config)#ip access-list extended OFFICE_ACL
This access list
will be applied to Router to filter traffic entering Management VLAN.
Task 2: Block all
telnet traffic from entering into the Management VLAN.
Telnet uses TCP port
23. We need to block all telnet traffic, not just from the two VLANs.
Router(config-ext-nacl)#deny
TCP any 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 eq 23
This blocks all
telnet traffic into the Management VLAN (192.168.10.0/24).
Task 3: Allow all
traffic From the Admin PC into the Management VLAN.
To allow a specific
PC, we need to use host wildcard mask or keyword "host" with the IP
address of the Admin PC as the source address.
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit
ip host 192.168.20.10 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
OR
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip 192.168.20.10 0.0.0.0 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
This allows all
traffic from Admin PC (192.168.20.10) into the Management VLAN
(192.168.10.0/24).
A host wildcard mask
0.0.0.0 is equal to subnet mask 255.255.255.255(/32) which means a single IP or
endpoint.
Task 4: Block SSH
traffic from the Reception PC to the Management VLAN but allow all other
traffic.
SSH uses TCP port
22. We need to use the "host" or host wildcard mask again for this
task.
Router(config-ext-nacl)#deny tcp host
192.168.20.30 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 eq 22
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit ip host
192.168.20.30 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
deny tcp host
192.168.2.30 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 eq 22: Blocks SSH traffic from Reception PC (192.168.20.30)
into the Management VLAN (192.168.10.0/24).
permit ip host
192.168.2.30 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255: Allows all other traffic from Reception PC (192.168.20.30) into the
Management VLAN (192.168.10.0/24).
Task 5: Allow HTTP
traffic from the Guest VLAN to the Management VLAN.
HTTP uses TCP port
80.
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp
192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 eq 80
This allows only
HTTP traffic from Guest VLAN (192.168.30.0/24) into the Management VLAN
(192.168.10.0/24).
Task 6: Block all
other traffic to the Management VLAN.
Router(config-ext-nacl)deny
ip any 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
This blocks all
other traffic destined for the Management VLAN (192.168.10.0/24).
Task 7: Apply the
Access List to the appropriate device interface.
An ACL applied
inbound on a VLAN interface filters traffic coming from the VLAN through the
VLAN interface.
An ACL applied outbound on a VLAN interface filters traffic going into the VLAN
through the VLAN interface.
We will apply the
access list outbound on the Management VLAN interface so that traffic from both
Office and Guest VLANs is filtered before it exits the Management VLAN
interface (G0/0.10) of the router and enters Management VLANs.
Router(config-ext-nacl)#exit
Router(config)#interface g0/0.10
Router(config-if)#ip access-group
OFFICE_ACL out
Router(config-if)#exit
ip access-group
OFFICE_ACL out: Applies the access list outbound on the interface.
Verification:
Verify by initiating
a telnet session from Admin PC to the server in Management VLAN. "remote host not
responding" should be shown.
C:\>telnet
192.168.10.10
Trying 192.168.10.10 ...
% Connection timed out; remote host not responding.
Now ping the server
from Admin PC, this should succeed.
C:\>ping
192.168.10.10
Pinging
192.168.10.10 with 32 bytes of data:
Request times out.
Reply from 192.168.10.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127
Reply from 192.168.10.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127
Reply from 192.168.10.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127
Now ping from Guest
PC, this should fail.
C:\>ping
192.168.10.10
Pinging
192.168.10.10 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from
192.168.30.1: Destination host unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.30.1: Destination host unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.30.1: Destination host unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.30.1: Destination host unreachable.
Now exit
configuration mode and save the configuration.
Router(config)#end
Router#write memory
Packet Tracer File
Clicking this button will begin the download of a ZIP file. Inside the ZIP file, you'll find a Packet Tracer Activity (.pka) file, which will automatically track your progress as you configure the network.

