IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing 1
Topology
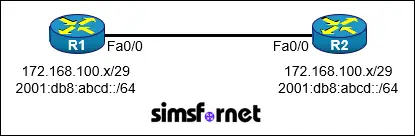
Tasks:
Configure IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity between two routers. For IPv4, use a /29 network from the 172.16.100.0/24 private range. For IPv6, use the EUI-64 method for generating the interface ID from the first /64 subnet of the 2001:db8:abcd::/48 prefix.
- Using FastEthernet0/0 on routers R1 and R2, configure the next usable /29 subnet from the 172.16.100.0/24 range. The network 172.16.100.0/29 is unavailable.
- For the IPv4 /29 subnet, router R1 must be configured with the first usable host address.
- For the IPv4 /29 subnet, router R2 must be configured with the last usable host address.
- For the IPv6 addressing, configure the routers using the EUI-64 method for IPv6 address generation on the Ethernet0/0 interfaces. Use the prefix 2001:db8:abcd::/64.
- Verify that pings work between the routers on both the IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges.
Solution:
Task 1: Using FastEthernet0/0 on routers R1 and R2, configure the next usable /29 subnet from the 172.16.100.0/24 range. The network 172.16.100.0/29 is unavailable.
The next /29 subnet after 172.16.100.0/29 is 172.16.100.8/29 which ranges from 172.16.100.9 - 172.16.100.15. The first usable IP is 172.16.100.9 and last usable IP is 172.16.100.14 as the 172.16.100.15 is the broadcast address of the subnet. The prefix /29 is equal to subnet mask 255.255.255.248.
Task 2: For the IPv4 /29 subnet, router R1 must be configured with the first usable host address.
Assign 172.16.100.9 to FastEthernet0/0 interface of R1 as its the first usable IP.
On R1:
R1#configure
terminalR1(config)#interface
f0/0R1(config-if)#ip
address 172.16.100.9 255.255.255.248R1(config-if)#no
shut
Task 3: For the IPv4 /29 subnet, router R2 must be configured with the last usable host address.
Assign 172.16.100.14 to FastEthernet0/0 interface of R1 as its the last usable IP.
On R2:
R2#configure
terminalR2(config)#interface
f0/0R2(config-if)#ip
address 172.16.100.14 255.255.255.248R2(config-if)#no
shut
Task 4: For the IPv6 addressing, configure the routers using the EUI-64 method for IPv6 address generation on the FastEthernet0/0 interfaces. Use the prefix 2001:db8:abcd::/64.
Enable IPv6 on the interface and assign an IPv6 address using EUI-64 method. The prefix given is 2001:db8:abcd::/64.
On R1:
R1(config-if)#ipv6
enableR1(config-if)#ipv6
address 2001:db8:abcd::/64 eui-64
Enable IPv6 on the interface and assign an IPv6 address using EUI-64 method.
On R2:
R1(config-if)#ipv6
enableR1(config-if)#ipv6
address 2001:db8:abcd::/64 eui-64
Task 5: Verify that pings work between the routers on both the IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges.
Test the connectivity between the routers by pinging.
R1#ping
172.16.100.14
Use show command show ipv6 interface
brief on R2 to check the EUI-64 generated address then ping from R1.
R1#ping
ipv6 2001:db8:abcd::<R2-EUI-64-generated-IPv6>
Now exit configuration mode and save the configuration
R1(config-if)#endR1#write
memory
R2(config-if)#endR2#write
memory
Packet Tracer File
Clicking this button will begin the download of a ZIP file. Inside the ZIP file, you'll find a Packet Tracer Activity (.pka) file, which will automatically track your progress as you configure the network.

